NEMA Ratings and What They Mean
Here’s our quick, in-a-nutshell rundown of the most commonly called-for NEMA ratings, and what each one means:
-
- NEMA 1: Indoor-use enclosures that protect internal components from solid foreign objects and contaminants (like falling dirt), and also provide limited protection to personnel by restricting their access to potentially hazardous components.
-
- NEMA 2: Indoor-use enclosures that restrict worker access to hazardous components, and protect the equipment stored inside against the ingress of solid foreign contaminants and dripping or lightly splashing water.
-
- NEMA 3: Indoor- or outdoor-use cabinets that limit personnel access to hazardous parts, and protect enclosed equipment from the ingress of contaminants like wind-carried dust and falling dirt, as well as moisture in the form of rain, sleet or snow. In addition, Type 3 enclosures are designed to remain undamaged even if ice forms on their outer surfaces.
-
- NEMA 3R: NEMA 3R enclosures are used indoors or outdoors, and not only provide workers with a degree of protection against making contact with hazardous parts, but also protect interior components from solid contaminants, water ingress in the form of rain, sleet or snow, and the formation of ice on the cabinet’s exterior.
-
- NEMA 3S: 3S enclosures are used indoors or outdoors, and help to protect personnel by limiting their access to potentially harmful components. They guard enclosed equipment against the ingress of windborne and falling solid foreign contaminants, like dirt and dust, as well as water in the form of rain, sleet or snow. In addition, the external mechanisms on NEMA 3S cabinets are required to remain operable even when ice-laden.
-
- NEMA 3X: Used either indoors or outdoors, these enclosures prevent the ingress of water in the form of rain, sleet or snow, as well as solid particulate like dirt and windborne dust. A NEMA 3X cabinet reduces risk to personnel by limiting access to hazardous components, provides internal components with an extra degree of protection against corrosion, and isn’t damaged by the formation of ice on its exterior surfaces.
-
- NEMA 4: Made for indoor or outdoor use, these cabinets and enclosures help prevent worker access to hazardous components, and guard against the ingress of water in the form of rain, sleet or snow, as well as water that is splashed or sprayed by hose. NEMA 4 enclosures prevent the entry of solid contaminants like dust and dirt, and are required to remain undamaged by the formation of ice on their outer surfaces.
-
- NEMA 5: Indoor-use enclosures that prevent personnel from accessing potentially dangerous components, and protect enclosed equipment from the ingress of solid foreign contaminants and objects like airborne dust, dropping dirt, lint, fibers, and fly-off particulate, as well as dripping or lightly splashing water.
-
- NEMA 6: These indoor or outdoor-use enclosures help prevent personnel from accessing hazardous parts, while protecting enclosed equipment against the ingress of solid foreign objects and water, whether exposed to hosing or temporary, limited-depth submersion. NEMA 6 cabinets must remain undamaged in the event that ice forms on the external surface of the enclosure.
-
- NEMA 6P: Made for indoor or outdoor use, these cabinets prevent workers from making contact with hazardous components, and help to block the entry of solid foreign matter, such as falling dirt. They also prevent the ingress of water, whether exposed to hosing or prolonged, limited-depth submersion. NEMA 6P enclosures provide an extra measure of protection against corrosion, and are required to remain undamaged in the event of exterior ice formation.
-
- NEMA 12: Knockout-free NEMA 12 enclosures are used indoors to help restrict personnel access to hazardous components, and protect enclosed equipment by preventing the ingress of solid foreign contaminants like airborne dust, dropping dirt, fibers, lint and fly-offs, as well as dripping and lightly splashing water.
-
- NEMA 12K: Indoor-use enclosures that are manufactured with knockouts and used to prevent personnel contact with hazardous components, as well as protect enclosed equipment from the ingress of solid foreign contaminants like dust, dirt, loose fibers, lint, fly-off particulate, and dripping or lightly-splashing water.
- NEMA 13: These indoor-use enclosures prevent workers from coming into contact with potentially hazardous components, and also protect enclosed equipment against the ingress of solid contaminants like dirt, dust, circulating fibers, lint, fly-off shavings, dripping or lightly splashing water, and oil and non-corrosive coolants that seep, spray, or are splashed.
For the complete specs and details on all of the NEMA enclosure ratings, check out their NEMA Enclosure Types report.
Here is explanation of NEMA rating.
IP Ratings Explained
Protect your electrical enclosure and its contents by knowing where and how it will be used so that you can order one with the correct IP Rating.
An IP (Ingress Protection) rating is used by buyers in Europe to specify the extent of protection an electrical enclosure has against environmental conditions.
The IP rating system was established by the International Electromechanical Commission (IEC), a worldwide organization for standardization. The object of the IEC is to promote International cooperation on all questions concerning standardization in the electrical and electronic fields. The IEC collaborates closely with the International Organization for Standards (ISO).
A complete description of the IP ratings and associated tests is found in IEC Publication 529. Although these ratings were initially developed as a way to classify enclosures, they now provide engineers with a convenient, practical way to compare levels of sealing. This standard describes a system for classifying the degrees of protection provided by the enclosures of electrical equipment. The adoption of this classification system promotes uniformity in methods of describing the protection provided by the enclosure and in the tests to prove the various degrees of protection.
Refer to the chart below for the ratings of relative protection of electrical enclosures:
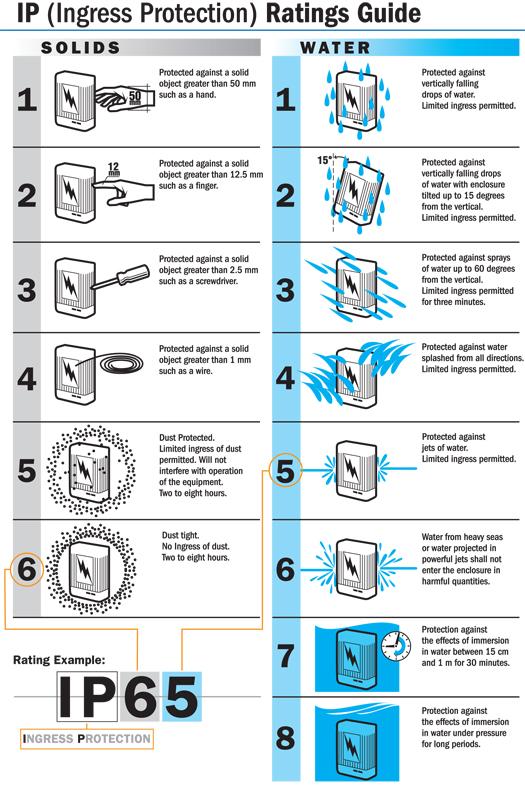
IP Ratings Guide
The IP rating normally has two (but may have three) numbers:
- Protection from solid objects or materials
- Protection from liquids (water)
- Protection against mechanical impacts (commonly omitted, the third number is not a part of IEC 60529)
Solids ingress protection Levels 5 and 6 are concerned with dust protection. Level 5 allows some dust to enter, but not enough to affect equipment operation. Level 6 is fully dust-tight. These tests are conducted in a dust chamber using fine talcum powder recirculated by a blower. Depending on the test requirements, a partial vacuum may be drawn through the enclosure. The vacuum tests are performed for a period of between two and eight hours, depending on how much air volume is drawn through the cabinet. The duration of the non-vacuum tests is eight hours.
IP water resistance varies from mild drip resistance, through sprays, jets, and total immersion. For spray Levels 3 and 4, the water is delivered by either an oscillating tube which looks like a garden sprinkler, or manually, by a handheld showerhead. The spray head passes 12.5 liters per minute. The enclosure being tested is exposed for at least three minutes, or in the case of a large unit, at least one minute for each square meter of surface as the spray head is slowly moved around.
For Levels 5 and 6, hose nozzles are used. The Level 5 exposure is at 12.5 liters/minute through a 6.3 mm (1/4 inch) nozzle. Level 6 is a higher pressure and flow test, using a 12.5 mm (1/2 inch) nozzle at a flow rate of 100 liters/minute. For both Levels 5 and 6, the hosing is conducted from a distance of 2.5 to 3 meters. Exposure time is three minutes.
For Levels 7 and 8 the enclosure is submerged in water. Level 7 tests water submersion for 30 minutes. The enclosure is dunked so that its bottom is 1 meter below the water surface, and its top is 0.15 meters below the surface. Level 8 is a special test where the performance level-in terms of duration and external water pressure (which is proportional to depth)-are agreed on by the vendor and the user.
IP First Number – Protection against solid objects; IP Second Number – Protection against liquids
For example, in an IP rating of IP 54 for an electrical enclosure, 5 describes the level of protection from solid objects and 4 describes the level of protection from liquids. In this case, 5 indicates the enclosure is designed and built for protection against dust limited ingress (no harmful deposit) while the 4 indicates limited ingress protection against low pressure jets of water from all directions.
An “X” can be used for one of the digits if there is only one class of protection, i.e. IPX1 which addresses protection against vertically falling drops of water e.g. condensation.
IP Rating Third Number – Protection against mechanical impacts (commonly omitted, the third number is not a part of IEC 60529)
Below are the third number IP ratings (IPXX1) and descriptions:
0 No protection.
1 Protects against impact of 0.225 joule (e.g. 150 g weight falling from 15 cm height).
2 Protected against impact of 0.375 joule (e.g. 250 g weight falling from 15 cm height).
3 Protected against impact of 0.5 joule (e.g. 250 g weight falling from 20 cm height).
4 Protected against impact of 2.0 joule (e.g. 500 g weight falling from 40 cm height).
5 Protected against impact of 6.0 joule (e.g. 1.5 kg weight falling from 40 cm height).
6 Protected against impact of 20.0 joule (e.g. 5 kg weight falling from 40 cm height).
IP Rating and NEMA Rating Comparison
IP Code Minimum NEMA Enclosure rating to satisfy IP Code
IP20 1
IP54 3
IP66 4, 4X
IP67 6
IP68 6P
The United States National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) also publishes protection ratings for enclosures similar to the IP rating system published by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). However, it also dictates other product features not addressed by IP codes, such as corrosion resistance, gasket aging, and construction practices. Thus, while it is possible to map NEMA enclosure rating/NEMA ratings that can satisfy or exceed the IP Code criteria, it is not possible to map IEC ratings (IP codes) to NEMA enclosure ratings, as the IP Code does not mandate the additional requirements. The table above indicates the minimum NEMA rating that satisfies or exceeds a given IP code, but can only be used in that way, not to map IP to NEMA.
By knowing the right IP rating for your electrical enclosure upfront you could save a whole lot on the back end – especially if your enclosure is going to be used in extreme weather conditions. Look for a product’s IP rating when making a purchase. The product’s IP rating is your way of knowing that the product is protected from particles or dust or water that may be present in the environment where you install the product. This is good to know, particularly when you’re designing your next enclosure for a buyer in Europe.