Last Updated on December 7, 2025 by Staff Writer
RFID Readers Kiosks 2022
One of our members is ELATEC and RFID Reader for Kiosks, Self-Service, Employees and Warehousing is their business, and has been for 34 years. We’ve used and quoted their readers hundreds of times (figure $150 or less). Chris Corsbie is our member representative and we want to introduce their product line (albeit somewhat condensed for pure kiosks).
He’s sent a couple of pieces of collateral including the obligatory brochure but also an informative whitepaper and a case study. And with all the attention these days on EV charging (and the massive funding behind it with NEVI e.g.) Chris put together a very helpful Six Questions To Ask when it comes to RFID readers and EV Charging. Those resources are listed/provided below
We also have been monitoring a wristband integration project by Olea Kiosks and turns out they just released a video showing the final engineered units, with a RFID reader integrated on the side.
RFID readers are mounted many different ways. Entering a building you will likely find them on the wall. There are many protocols and over the years companies have done their best to promote their favorite. The DOD uses CAC (Common Access Card). But then RFID readers were engineered for multi-protocol and the brand of RFID reader became less and less critical.
The history of RFID is fascinating too. Goes back to the Cold War.
Here is quick video off the Olea production floor showing unit that reads wristband RFID chip. If you are interested we also have a video showing a kiosk engineered with two (2) wristband printers as well.
Brief background on ELATEC:
- 60+ Transponder Protocols along with Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
- 110 Countries
- Strong partnership with HID
- ELATEC has remotely programmable readers, eliminating touch labor costs
- ELATEC is a world leader in RFID readers for user authentication and access control. We have a 34-year track record. Our global HQ is in Germany, and our HQ for the Americas is in Florida.
- We’ve been in the US for @8 years, initially primarily in secure printing, and for the past four years, successfully penetrating most of our numerous “new” market verticals.
- Target markets are the kiosk/vending/dispensing/automated locker market
- Our RFID readers for kiosk applications are ideal in “closed environments” where RFID badges (or mobile credentials) are used by staff or members. (How RFID works)
- ELATEC RFID readers offer some real advantages over competitor readers.
Brochures, Whitepaper and Case Study for RFID
Note that we compress fairly aggressively so sometimes there is some loss of fidelity.
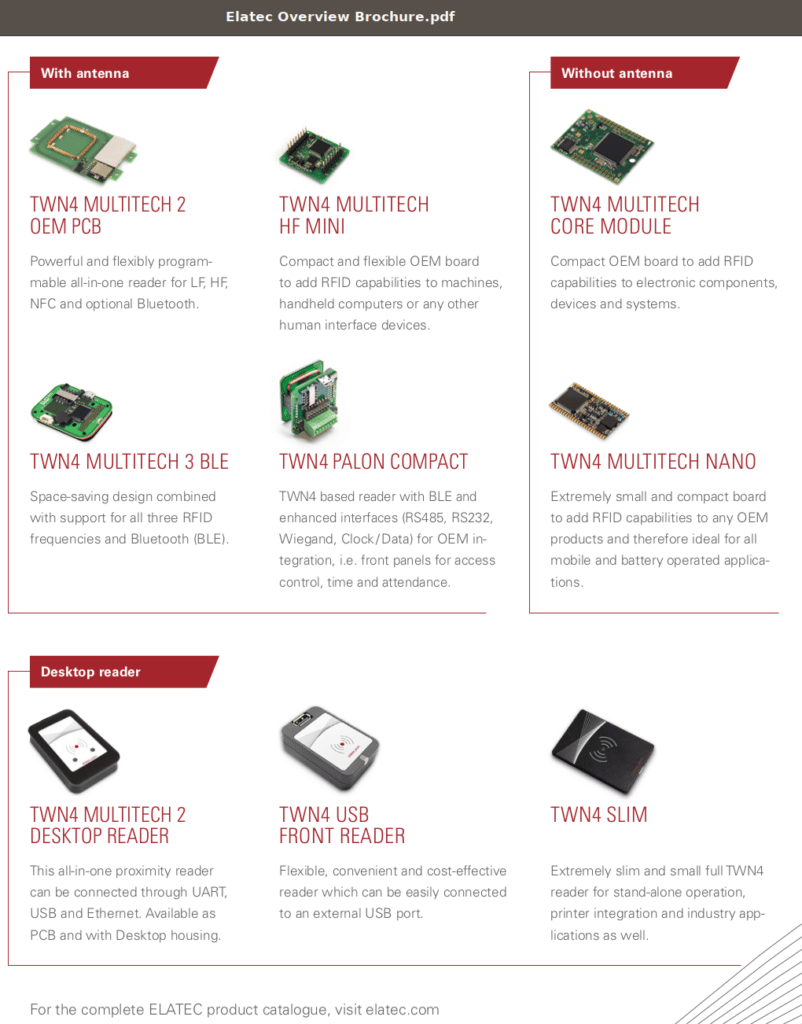
- Elatec Overview Brochure-compressed
- SECURE SELF-SERVICE WITH RFID WHITEPAPER-compressed
- Kiosk-Industrial Vending Case Study-compressed
Product Catalog
Contact Information
Americas
ELATEC Inc. • 1995 SW Martin Hwy • Palm City, FL 34990 • USA
Phone: +1 614 809 3352 • Direct: +1 614 809 3352
E-Mail: [email protected] • Website: elatec.com
EMEA
ELATEC GmbH
Zeppelinstraße 1
82178 Puchheim
Germany
P +49 89 552 9961 0
F +49 89 552 9961 129
[email protected]
Offices in Shenzen, Tokyo and Austrialia
For More Information
- You can always email [email protected] with your request
More Posts
- RFID Readers for EV Chargers: Six Questions to Ask(Opens in a new browser tab)
- Kiosk RFID News – Elatec U.S. Production Facility Ships First 100,000 RFID Units(Opens in a new browser tab)
- RFID Kiosk Technology in Retail(Opens in a new browser tab)
Tell Me More About RFID Protocols [from RFIDjournal]
The protocols are called the air-interface protocols, and there are many “standards” for such protocols, depending on the type of RFID system used. Here are a few of the most common air-interface protocol standards ratified by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO):
ISO 14443: This high-frequency (HF) standard is designed to have a short read range and include encryption, since it was created for proximity cards. What that means is that it was created for secure payments.
ISO 15693: This HF standard was developed for vicinity cards. It has no encryption and a longer read range than ISO 14443-based systems. It is used in many access-control systems, but has also been employed for inventory management and other applications.
ISO 18000-3: This HF standard, developed for item management, has never really caught on. Most companies simply use ISO 15693 for item management.
Near Field Communication: While not an official ISO standard, NFC is based on ISO 14443 and adds some additional capabilities, such as the ability of a reader to emulate a tag. NFC will also incorporate ISO 15693 over time, so you will be able to use an NFC-enabled phone to enter a building.
ISO 18000-6C: This ultrahigh-frequency (UHF) standard is based on the EPC Gen 3 air-interface protocol. Although there is an ISO 1800-6A and an ISO 1800-6B, it is ISO 18000-6C that is widely used for passive UHF systems.
ISO 24730: This protocol governs the communication of active RFID transponders operating at 2.45 GHz, and is used in real-time location systems.
There are other standard and proprietary air-interface protocols, but these are the main ones currently being used.
Some History of RFID [from Paragon]