
The Disabled and Impaired Population 2023
We are always looking to improve accessibility and one method to do that is to establish the population segments with what impairment. The most good for the most people is a good starting point. Where do differences in accessibility manifest and to what degree. Generally, there are these main categories:
The five senses are the traditional senses that humans have to react to their environment. They are:
- Sight: allows us to see the world around us.
- Hearing: allows us to hear sounds.
- Smell: allows us to detect smells.
- Taste: allows us to detect the flavors of food.
- Touch: allows us to feel the world around us.
There is an argument to be made for a sixth sense — which would be your brain.
Disabilities Are Different
Some of the most common types include:
- Physical disabilities: These disabilities affect a person’s ability to move around or use their body. Examples of physical disabilities include:
- Mobility disabilities: These disabilities make it difficult or impossible for a person to walk or move around independently. Examples of mobility disabilities include: paraplegia, quadriplegia, and cerebral palsy.
- Limb loss: This disability refers to the loss of one or more limbs. Examples of limb loss include amputations and congenital limb deficiencies.
- Visual impairments: These disabilities affect a person’s ability to see. Examples of visual impairments include: blindness, low vision, and color blindness.
- Hearing impairments: These disabilities affect a person’s ability to hear. Examples of hearing impairments include: deafness, hard of hearing, and tinnitus.
- Intellectual disabilities: These disabilities affect a person’s cognitive abilities. People with intellectual disabilities may have difficulty learning, understanding, and communicating.
- Mental health disabilities: These disabilities affect a person’s mental state. Examples of mental health disabilities include: depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia.
- Autism spectrum disorder: This disability affects a person’s social communication and interaction skills. People with autism spectrum disorder may also have sensory sensitivities and repetitive behaviors.
These are some of the many types of disabilities that humans can have. It is important to remember that people with disabilities are just as diverse as any other population group. They have different abilities, strengths, and challenges. It is also important to remember that disability is not a weakness. It is simply a different way of being.
There is no single accepted definition of disability. Different definitions and disability questions may identify different populations with disabilities and result in larger or smaller estimates.
Cornell Definitions
Below are the six questions used in the ACS to identify persons with disabilities. Note that the Census Bureau refers to each of the individual types as “difficulty” while in this report the term “disability” is used.
- Hearing Disability (asked of all ages):
- Is this person deaf or does he/she have serious difficulty hearing?
- Visual Disability (asked of all ages):
- Is this person blind or does he/she have serious difficulty seeing even when wearing glasses?
- Cognitive Disability (asked of persons ages 5 or older):
- Because of a physical, mental, or emotional condition, does this person have serious difficulty concentrating, remembering, or making decisions?
- Ambulatory Disability (asked of persons ages 5 or older):
- Does this person have serious difficulty walking or climbing stairs?
- Self-Care Disability (asked of persons ages 5 or older):
- Does this person have difficulty dressing or bathing?
- Independent Living Disability (asked of persons ages 15 or older):
- Because of a physical, mental, or emotional condition, does this person have difficulty doing errands alone such as visiting a doctor’s office or shopping?
Note:
- The “Any Disability” category used in this report includes persons who reported one or more of the individual disability types.
- Respondents could report more than one disability type.
- Some disability questions were not asked of children.
- A separate set of survey questions identify veterans with service-connected disabilities. Based on a separate set of survey questions, this report includes estimates related to veterans’ service-connected disability
There are many types of disabilities, such as those that affect a person’s:
- Vision
- Movement
- Thinking
- Remembering
- Learning
- Communicating
- Hearing
- Mental health
- Social relationships
Although “people with disabilities” sometimes refers to a single population, this is actually a diverse group of people with a wide range of needs. Two people with the same type of disability can be affected in very different ways. Some disabilities may be hidden or not easy to see.
According to the World Health Organization, disability has three dimensions:1
- Impairment in a person’s body structure or function, or mental functioning; examples of impairments include loss of a limb, loss of vision or memory loss.
- Activity limitation, such as difficulty seeing, hearing, walking, or problem solving.
- Participation restrictions in normal daily activities, such as working, engaging in social and recreational activities, and obtaining health care and preventive services.
What Does The CDC Say
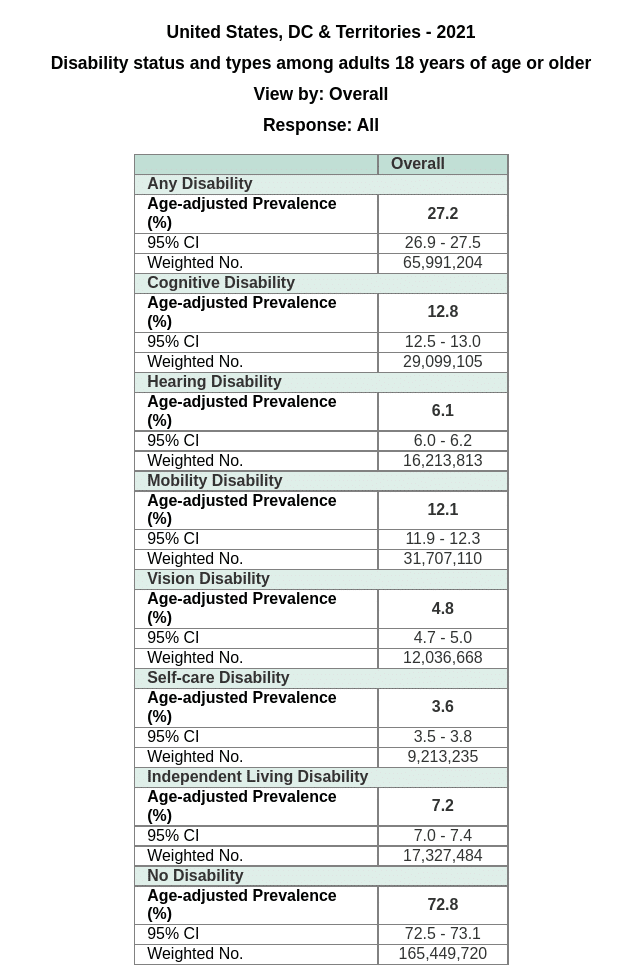
CDC Data
Here is a disability breakdown from 2022
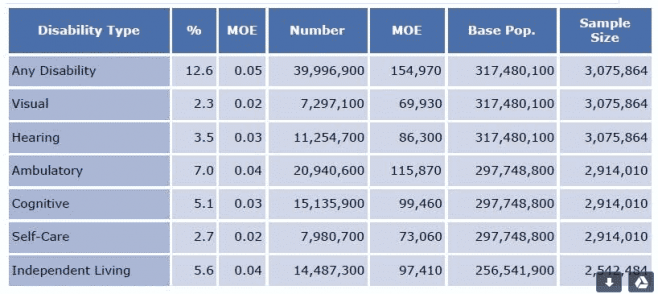
Click for full size
Other Datasets Used in The U.S.
- DisabilityStatistics.org, which is managed by Cornell University’s Institute on Employment and Disability. This site is extremely useful for searching through a number of different data qualifications and demographics. The primary downside is that the data tends to be a few years old by the time it is published on the site.
- Annual Disability Statistics Compendium, which is compiled by the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability. This source is more frequently updated, but isn’t quite as interactive. New Hampshire Disabled 2023 (PDF) — Accessible-Annual Report — 2023 — Accessible
All Well and Good for U.S., but what about the Rest of the World
- Disability – Office for National Statistics (ons.gov.uk)
- UK disability statistics: Prevalence and life experiences – House of Commons Library (parliament.uk)
- Disability facts and figures | Disability charity Scope UK
- Worldwide data from the WHO — and here is their disability WHO 2011_eng-compressed
It was a bit of a challenge using the Office for National Statistics. Fortunately they offer assistance
There are several ways that you can access Census 2021 data : Office for National Statistics website – census hub
This will take you to the main website from which you can navigate your way to the census data using the Census Topics listed or the Get data link.
The Census 2021 topic summaries are sets of data and supporting information, grouped by a similar theme. The first topic summary was released on 2nd November 2022. Please see the following links for datasets for these topics.
- demography and migration
- UK armed forces veterans
- ethnic group, national identity, language, and religion
- Welsh language
- labour market and travel to work
- housing
- sexual orientation and gender identity
- education
With regards to your query, data is available from the health, disability, and unpaid care topic summary.
Please see the following links to Census 2021 datasets:
TS038 – Disability – All Lower Tier Local Authorities in England and Wales.
- Please use this link to access this dataset on the Office for National Statistics website.
TS038 – Disability – England and Wales.
- Please use this link to access this dataset on the Office for National Statistics website.
TS038 – Disability – All the regions in England and Wales.
- Please use this link to access this dataset on the Office for National Statistics website.
If you find that the category for a topic isn’t available in some of the univariate datasets or they are in fact not detailed enough, you may find the data required through the ‘Create a custom dataset‘ tool instead. This feature allows you to build a custom univariate or multivariate dataset from the ground up, subject to disclosure control. This is applied to ensure we are protecting personal data in our published statistics.
By default, all of the datasets given in this email are set at a lower tier local authority geography level. This means they show data for all local authorities within England and Wales. Although this is the case, it is possible to change the geography level so that it meets your preferences.
Subject to disclosure control, you are able to make these datasets as broad or precise as you like. To do this, simply click on the blue ‘change’ text that is listed in the ‘Area type’ and ‘coverage’ rows. To assist you in doing this I have attached navigation instructions to the ONS (Office for National Statistics) website to this email.
Please see the following Census 2021 datasets:
Age ( 86 categories) by Disability by Sex – All Lower Tier Local Authorities in England and Wales
- Please use this link to access this dataset on the Office for National Statistics website.
Age ( 86 categories) by Disability by Sex – England and Wales
- Please use this link to access this dataset on the Office for National Statistics website.
Age ( 86 categories) by Disability by Sex – All Regions in England and Wales
- Please use this link to access this dataset on the Office for National Statistics website.
Please see a link to our Census 2021 dictionary where you will find information to all the definitions, variables, and classifications to help when using Census 2021 data.
Other Census 2021 data can be found on the Nomis Website: 2021 Census Data This webpage will give you the option to choose from either the Topic Summaries (univariate data), the Ready Made Tables (multivariate data), Non-UK Short-term Residents and Bulk Data Downloads. It will be added to as further data are released. Nomis is a service run by Durham University on behalf of the Office for National Statistics.
I have attached navigational as well for the Nomis website (see attachments below) and as set on How to use the Create a Custom Dataset tool should you wish to explore further Census data.
You may also be interested in the following census analysis:
- Disability by age, sex and deprivation: England and Wales: Census 2021 https://www.ons.gov.uk/releases/disabilitybyagesexanddeprivationenglandandwalescensus2021
I have carried out further research and found there is data on specific disabilities on the Public Health England or NHS Data dashboards websites. Please note we are unable to comment upon figures not produced by the Office for National Statistics (ONS).
If you have any further queries or have difficulty in obtaining any data, please don’t hesitate to get in touch.
Attachments Below for ONS UK
Nomis Navigation Instuctions 2021 v2.1
ONS – Create a Custom Dataset Navigation Instructions V1.0
ONS Navigation Instructions – 2021 v4
How Do Kiosks Address Disabilities?
- Tactile navigation aids
- Audio via headphone jack or speakers
- Screen reading (audio playback)
- Screen reading (captions)
- Microphones for noise discrimination and cancellation
- Braille — typically strips but newer forms available
- Biometrics
- Speech on Demand for print disabilities
- Physical reach with height and depth
- Physical access via angular presentation
- Location physical positioning
- Multi-lingual language
- Facial navigation (blinking your eyes)
- Gestures
- Contrast, Color and Fonts – UX in general
- Screen Magnification and Zoom
- Sign Language
- Adjusting for different personas
- Required testing prior to deployment by multiple user groups
- augmented reality
- Haptic touchscreens
- AI Assist
- Many other ways
- Self-Driving Cars is a big one these days
Contributors
It’s important to establish a consensus of input and thoughts from a variety of involved parties. We very much thank the following.
- Mary Jo Barry with Dolphin — Our industry is fully equipped to address disabilities of any nature, we have the technology. Dolphin values the collaboration that exists within the KMA because working with colleagues who cover the spectrum of parts and pieces that create an integrated kiosk solution provides us the context and perspective to dream a bigger dream. Dolphin envisions a future where kiosks are universally designed from the start to be accessible to people with physical disabilities and neurodivergence. Just as curb cuts have benefited more than wheelchair users, we believe changing legislation is an opportunity to improve the lives of anyone who cannot use a self-service kiosk, for any reason.”
- Jim Kruper with KioWare (supports JAWS) — Wow, nice to have so much information in one place – definitely a page to be bookmarked. When it comes to accessibility I tend more to collecting data than providing data; i.e., I am not an expert, so I don’t have an opinion on anything missing or misstated. It all looks very good to me.
- U.S. Access Board — The data from CDC is among the most detailed and useful for disability incidence that you will find. You should cite the CDC as you have done at your URL.
- Sabine Croxford with the RNIB — Thanks Craig for your message. I have asked our research team and they have pointed me to the following links (see the UK links above). Sabine is a User Experience Evaluator at RNIB
- Rachael Bradley Montgomery, Ph.D. — It looks like you’ve pulled the updated US numbers. The problem is all the numbers are underreported and the diversity of disabilities is not captured.
- NFB (archivist) Nichole — Non-profit Organization Management, Baltimore, MD
What About ADA regulations and Legal Consequences
The quick update is that the DOJ issued NPRM on web and mobile last week. The US Access Board is releasing ADA proposal for EV Charging on September 1st, and the “pre-final” for Self-Service kiosks and POS new rules by U.S. Access Board are to be released December 1st of this year.
- ADA – Web Accessibility & Mobile Accessibility
- Restaurants ADA Compliant
- ADA Kiosk & Accessibility Update – New technology, tradeshows, Braille pad and more
- Legal Actions
- Touchscreens and PIN in the UK
Related Posts
- Disability Inclusion In Workplace Interview(Opens in a new browser tab)
- POS ADA Accessibility, Consumers & Payment Terminals – Biometric Payment(Opens in a new browser tab)
- Self-Check Hearing Screening Kiosks Going Into Giant Eagle(Opens in a new browser tab)
- ADA Kiosk – UX for Disabled Webinar from Paciello Group April 25(Opens in a new browser tab)
- Kiosks and people who are blind or partially sighted(Opens in a new browser tab)
Assistive Technology Solutions by the Association
- KioWare – built-in JAWS Kiosk support & Storm AudioPad for ready-made browser functionality. Also noTouch KioTouch
- Vispero – The world’s leading assistive technology provider for people who are blind or who are partially sighted.
- JAWS Kiosk is focused on delivering accessible kiosk solutions whether it’s through the incorporation of Freedom Scientific’s industry-leading screen reading software, JAWS®, or by utilizing TPG’s accessible design and technical implementation services.JAWS Kiosk Software –
- TPGi — a subsidiary of Vispero, TPG Interactive (TPGi) is a world-class accessibility solutions provider with a reputation for excellence. We help clients achieve end-to-end accessibility in their digital assets (websites, software applications, mobile applications, documents, etc.) and assist in embedding accessibility into their processes and procedures. Whether you are new to accessibility or mature in your accessibility processes, TPGi can assist your organization.
- Storm Interface — Storm Interface develops and manufactures responsive human interface devices for use in a wide range of public and industrial applications. The company’s award-winning products are now globally deployed, internationally recognized and widely acclaimed.
- Tech For All Consulting — For over 15 years, TFA’s expert teams have been providing consulting services to its clients to ensure the accessibility and usability of their products, websites, mobile apps, kiosks, and services. Tech for All’s Accessibility Compliance and Universal Design Services — Web, Mobile, and Multiplatform Applications — Kiosk and Self-Service Systems — Training — Planning and Strategy
- Dolphin Kiosk — Welcome people who are blind and partially sighted into your business by enabling them to engage with your self-service points through Dolphin Accessible Kiosks fully. Dolphin Accessible Kiosks can deliver a range of support—magnification, speech and full screen-reading—without expensive retrofits. SuperNova differentiates itself from other kiosk accessibility software through crystal clear magnification at any level, unrivaled intuitive touchscreen capabilities, 24 changeable color themes and full screen-reading with human-sounding voices. It’s also fully compatible with Storm AudioNav Keypads and the SuperNova API is customizable for your bespoke kiosk projects.
- MimoMonitors — Haptic Touchscreens — The first of its kind, this new 10.1” touchscreen leverages the durability, reliability, and quality of the Mimo Vue display and the groundbreaking technology of TanvasTouch to allow users to feel what they see on screen. The result is a multisensory experience that brings touch to life on a new dimension.
- dot inc. — Assistive Technology to build Barrier-free world. Design with the user’s eye level in mind. Automatic and manual use provided for user’s ease and convenience. Braille, tactile, sign language, voice guidance, large font size Barrier-free features for all.
- Voice Software
Disabled Data Worksheet
We did our own compendium xls and it can be fairly difficult to correlate the overall population numbers and breakouts. Often sources call out percentages but never say percentages of what. Sometimes they don’t add up. For example, the CDC says population with No Disability is 166 Million. Then they say population with Any Disability is 66 Million. That’s 232 Million. Population in U.S. is around 330 Million right?
